Nanotechnology
Determination of Isoelectric point
EGP1,000.00The isoelectric point (pI) is the pH of a solution at which the net charge of a zwitterion molecule (e.g. amino acids, peptides, proteins) becomes zero. At solution pH that is above the pI, the surface of the molecule is predominantly negatively charged, while it becomes positively charged when the solution pH is lower than the pI.
Identifying the isoelectric point of your molecule can help in several ways:
- For protein purification, where proteins have minimal water solubility at their pI.
- Study the best level of outer charge for your application
Nanomaterials (Powder form)
EGP570.00 – EGP2,850.00 / 5g powderThe use of nanomaterials has become the core of scientific research in many disciplines. Through our network of collaborators, Nawah hereby provides the following nanomaterial in the powder form. Each batch comes with a certificate of size by Nawah Scientific. (price is mentioned, least amount to order is 5g).
Nanomaterials (Suspension form)
EGP400.00 – EGP1,300.00 / 5ml suspensionThe use of nanomaterials has become the core of scientific research in many disciplines. Through our network of collaborators, Nawah hereby provides the following nanomaterial in the suspension form. Each batch comes with a certificate of size by Nawah Scientific. (price is mentioned, least amount to order is 5ml).
Particle size and zeta potential measurement
EGP130.00 – EGP225.00 / sampleThe world’s most widely used particle analyzer!
The Zetasizer Nano ZS is a high performance two angle, particle size, zeta potential and molecular weight analyzer. Ideal for the measurement of small volume samples, samples at very low or high concentration and the detection of aggregates. Using Non-Invasive Backscatter optics (NIBS) it has significantly better performance than systems using 90 degree scattering optics.
Preparation of Nano Drug Delivery Systems
Owing to the rapid development of nanoscience and outstanding performance of nanomaterials, nanotechnology has become a new solution to overcome the limitations of traditional dosage forms. Nano-drug delivery systems (NDDSs) are a class of nanomaterials that have abilities to increase the stability and water solubility of drugs, prolong the cycle time, increase the uptake rate of target cells or tissues, and reduce enzyme degradation, thereby improve the safety and effectiveness of drugs. NDDSs can be administered by various routes including inhalation, oral administration, or intravenous injection, remaining better bioavailability.
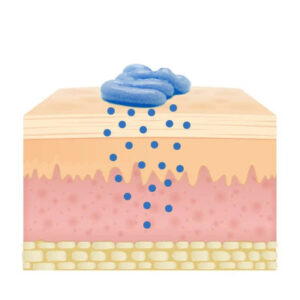
Skin Deposition Test (Stripping Technique)
EGP6,500.00With the remarkable interest in the development of innovative pharmaceutical products, suitable methods need to be established to evaluate the fundamental physicochemical parameters required in pre-formulation studies. In the case of topical formulations, for which the drug is intended to act directly on the skin, evaluation of the drug deposition in the different skin layers is critical to establish dermal bioavailability and thereby make an approximation of the effectiveness.
Methodology
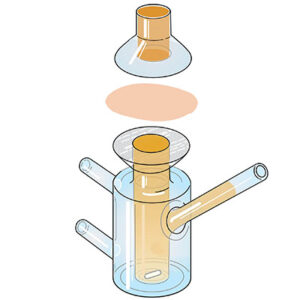
Skin deposition or retention experiments are performed ex-vivo using Franz diffusion cells and rat skin. The tested formulation is typically added to the donor compartment and incubated with the skin for a predetermined interval. At the end of the experiment, skin is removed and separated into the three different layers, namely the stratum corneum, epidermis and dermis. Each layer will be extracted with the suitable method and drug concentration will be determined in each individual layer.
Experiment is carried in triplicate and individual results as well as averages are reported.
Skin Permeation Test (Franz Cell Technique)
EGP4,600.00 / sampleEx-vivo skin permeation experiment of a loaded drug is an important benchmark for the prediction of percutaneous absorption during the development of transdermal formulations. It gives an idea of the potential steady state concentration following the percutaneous absorption from the tested formulation. It can be a very valuable tool for testing the bioequivalence of developed formulations versus marketed products.
Methodology
Skin permeation experiments are carried out using Franz diffusion cells and rat skin. The receptor compartment to be filled with the chosen receptor medium (depends on the physicochemical properties of the loaded drug) and the tested formulation will be inserted in the donor compartment. Samples will be withdrawn from the receptor compartments at different time intervals up to 24 hours. Drug permeated will be analyzed using HPLC. This allows the establishment of the ex-vivo permeation profile of the loaded drug with the subsequent calculation of the flux rate and the total amount permeated.
Experiment is carried in triplicate and individual results as well as averages are reported